Everything You Need To Know About Rabbit Teeth
Rabbits are prone to dental problems, although the symptoms are typically overlooked. Here’s how to keep your rabbits’ teeth in good shape and recognize the signs of a problem.
What is special about the rabbit’s teeth?
 The teeth of a rabbit never stop growing! Many people assume that chewing is necessary for keeping their teeth short. While they like chewing, a rabbit’s teeth are kept short by typical wear from where their top and bottom teeth connect.
The teeth of a rabbit never stop growing! Many people assume that chewing is necessary for keeping their teeth short. While they like chewing, a rabbit’s teeth are kept short by typical wear from where their top and bottom teeth connect.
What should a rabbit’s tooth look like?
Rabbits have 28 teeth that are permanent. Rabbits, guinea pigs, and horses, for example, have long, continuously growing teeth that are extremely long above and below the gum line. The incisors, or front teeth, are the most visible, but rabbits also have molars in the back of their mouths, which can cause problems because they are more difficult to see.
Do rabbits only have 4 teeth?
No, rabbits do not only have 4 teeth, although this misconception is understandable as the most easily seen teeth are 4 teeth at the front. The incisors are the large front teeth. Although they grab all the attention, an adult rabbit has a complete set of 28 teeth. There are a total of six incisors: two on top, two on the bottom, and two “peg teeth.” These are very small teeth that are situated just beneath the upper incisors. Rabbits also have 12 upper and 10 lower “cheek teeth” down the sides of their jaws.
Rabbits eat hard, fibrous vegetation and utilize their incisors to do so, which have sharp edges, to slice through it like scissors. Their cheek teeth aid in the chewing of food into smaller, easier-to-swallow chunks.
In the wild, this set of teeth comes in handy. Because rabbits are herbivores who eat rough foliage, this is the case. Rabbits, like Bugs Bunny, would love to eat carrots all day. However, the majority of them are obliged to eat other meals in order to survive. Fibrous grasses, weeds, hay, leaves, twigs, and even tree bark are among their favorite foods. They wear their teeth out by eating this type of food.
Do rabbit teeth need to be trimmed?
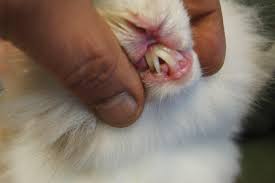 When a rabbit consumes fibrous plants, the natural grinding process wears down the teeth just enough to keep them at an appropriate length despite their constant growth. However, due to a variety of health, environmental, and hereditary variables, pet rabbits’ teeth must frequently be manually trimmed.
When a rabbit consumes fibrous plants, the natural grinding process wears down the teeth just enough to keep them at an appropriate length despite their constant growth. However, due to a variety of health, environmental, and hereditary variables, pet rabbits’ teeth must frequently be manually trimmed.
While all of your rabbit’s teeth might become too long, the incisors are the easiest to spot when they do. They have the potential to grow so long that they coil up and protrude between your rabbit’s lips. This is a concern since they can get stuck on objects like cage bars or, even worse, develop into your rabbit’s gums or mouth roof.
The molars, like the incisors, can grow to be excessively long. 2 Because the molars are difficult to view without using a speculum to look at them at the rear of the mouth, rabbit owners are frequently unaware of these teeth are enlarged. Rabbits and other exotic pets with overgrown teeth drool a lot and have trouble eating and swallowing, so keep an eye out for these symptoms in your rabbit. Ileus can develop quickly if a rabbit is unable to eat, posing a life-threatening situation.
How often do rabbits need their teeth trimmed?
It may be feasible to cut your rabbit’s teeth if they are overgrown. This is a completely painless procedure since their teeth are formed differently than humans. Sedation isn’t always necessary. If your rabbit has a bad form of malocclusion, you may need to visit the vet on a regular basis for clipping.
Rabbits need their teeth trimmed at least once a month for some rabbits. However, because this surgery can be stressful for rabbits, your veterinarian may urge that the maloccluded teeth be removed entirely.
Why do rabbits bite their owners?
 Rabbits bite for a number of different reasons. It is common for rabbits of any age to bite because of raging hormones that influence their behavior. A rabbit’s bite can also be caused by stress. To avoid an uncomfortable circumstance, a stressed rabbit may bite or lunge. To avoid this behavior, owners should interact with rabbits in a calm and calming manner. Usually, rabbits bite to assert authority, guard their food, or protect themselves from predators.
Rabbits bite for a number of different reasons. It is common for rabbits of any age to bite because of raging hormones that influence their behavior. A rabbit’s bite can also be caused by stress. To avoid an uncomfortable circumstance, a stressed rabbit may bite or lunge. To avoid this behavior, owners should interact with rabbits in a calm and calming manner. Usually, rabbits bite to assert authority, guard their food, or protect themselves from predators.
For no apparent reason, a dominating bunny may bite an owner. When their owners come too close to the rabbit’s territory, indoor rabbits may nibble at their hands and/or feet. Dominant rabbits may also bite humans in this manner to warn them to leave an area.
Avoiding rewarding the rabbit for biting is the most crucial step in addressing this habit. When a rabbit bites you, it’s tempting to flee, yet this only promotes the biting habit. Instead, you should demonstrate your control over the bunny by doing the following:
- When the rabbit bites you, make a lightly startling sound.
- For a few seconds, place your palm on top of the rabbit’s head and gently press it to the floor. This activity will teach your bunny that you are the dominant partner in your relationship.
- Give your rabbit a little time-out in its cage. If the first two steps haven’t worked, try this one. Your rabbit should link excellent behavior with the opportunity to leave its cage.
- Neutering or spaying your rabbit. The hormones that control reproductive behavior are altered. These hormones can make it more likely for a rabbit to acquire a biting habit.
Do rabbit bites hurt?
 Nips from rabbits are usually harmless. They’re not meant to injure or maim people; instead, they’re meant to interact with them. Bite, on the other hand, is a different story.
Nips from rabbits are usually harmless. They’re not meant to injure or maim people; instead, they’re meant to interact with them. Bite, on the other hand, is a different story.
When a rabbit gives a real bite, its jaw opens wide and clamps down forcefully. They hold closely at times and are hesitant to let go. It’s an indication that the bunny is afraid or furious. Is it painful to be bitten by a rabbit? Yes, however, it depends on your level of pain sensitivity. However, most people would agree that a genuine rabbit bite is painful.
Rabbits have long, pointed teeth that help them cut through tough leafy plants. When the necessity comes, they can simply cut through the skin. Rabbit bites frequently bleed a lot and take a long time to recover.
A bite from a baby rabbit isn’t as painful as bites from an adult rabbit. This is due to the fact that their teeth are smaller. Dwarf rabbits differ from bigger varieties in this regard. It also depends on how aggressively the rabbit bites. If the rabbit is afraid, he or she may bite harder than if surprised. Whatever the situation may be, you’ll know if your rabbit bites you.
https://www.rabbitproducersassociation.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-rabbit-teeth/https://www.rabbitproducersassociation.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/rabbits-teeth-7.jpghttps://www.rabbitproducersassociation.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/rabbits-teeth-7-150x150.jpgUncategorizedRabbits are prone to dental problems, although the symptoms are typically overlooked. Here's how to keep your rabbits' teeth in good shape and recognize the signs of a problem. What is special about the rabbit's teeth? The teeth of a rabbit never stop growing! Many people assume that chewing is necessary...Netherland Dwarf Rabbit domains@dmhubtraining.comAdministratorNetherland Dwarf Rabbit



Leave a Reply